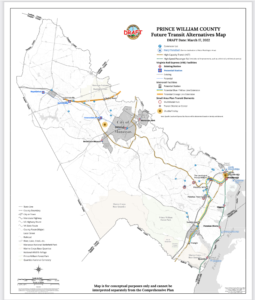
Prince William County’s Proposed “Future Transit Alternatives Map” Dated March 17, 2022
On April 15, 2022, Active Prince William submitted the following public comments on the draft “Future Transit Alternatives Map” that defines the public transportation element for the update to Prince William County’s Comprehensive Plan known as “Pathways to 2040”.
1) The Future Transit Alternatives Map needs to identify specific sites for proposed High-Capacity Transit stations that would exist by the year 2040.
The Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments needs to accept those sites on its map of High Capacity Transit Station Areas and to agree that they qualify as “Regional Activity Centers” (using the MWCOG definition of that term), so Prince William’s 2040 Comprehensive Plan is consistent with the Metropolitan Washington Planning Framework for 2030.
Unless specific station sites are identified, the Mobility Chapter will not be integrated with the Land Use and Housing Chapters. Identifying the planned locations of future VRE and Metrorail stations is required for the Land Use Chapter (including Land Use Map) to specify where new Transit-Oriented Development (TOD) will be planned within walking distance of High-Capacity Transit Stations. Identifying the planned locations of future VRE and Metrorail stations is required for the Housing Chapter to plan to meet regional housing targets set with MWCOG.
 MWCOG’s Regional Housing Targets
MWCOG’s Regional Housing Targets
2) The Future Transit Alternatives Map should clarify if all projects shown on the map are planned to be completed by 2040. If some projects will have a longer time frame, then the projects planned to be completed by 2040 should be identified clearly or included on a separate map. In particular, the proposed extensions of the Metrorail Orange Line and the VRE Manassas Line are redundant, and both are likely unnecessary with the advent of the I-66 Express Lanes. The Future Transit Alternatives Map should clearly identify that the existing I-95 and imminent I-66 Express Lanes are “existing” High-Capacity Transitways.
Knowing what projects are expected to be built over the next 20 years is necessary so other Comprehensive Plan policies, action strategies, and projects can be budgeted and synchronized. Maps showing planned roads and trails should also identify projects planned for completion by 2040, plus other aspirational projects using the same approach for transit projects.
3) The Mobility Chapter should include action strategies to acquire right-of-way for the proposed route of the Orange Line to Gainesville or that project should be removed from the map. Unless located within the I-66 right of way, the right-of-way for the Orange Line extension may require going through Bull Run Regional Park, Manassas National Battlefield Park, and/or high-value commercial properties. Fairfax County committed almost $60 million to preserve right-of-way along the I-66 corridor for extending Orange Line to Centerville during expansion to create Express Mobility Partners toll lanes, but Prince William preserved no right-of-way–suggesting a proposal for extending the Orange Line to Gainesville is more of a fantasy than an actual plan.
4) If the proposed route of the Orange Line to Gainesville remains on Future Transit Alternatives Map , then the Land Use Chapter should include plans for town centers with T-5 and T-6 Transect Zones at the station locations.
5) The Mobility Chapter should define the southern terminus of the proposed Blue/Yellow Line in eastern Prince William, and that terminus should subsequently be identified in the Visualize 2045, TransAction, and VTrans plans.
6) The Mobility Chapter should include action strategies to acquire right-of-way for the proposed route of the Blue/Yellow Line to Triangle or of the proposed BRT system.
7) The proposed route of the Blue/Yellow Line to Triangle , or of the proposed BRT system, should be clarified so it will be clear what land parcels will be suitable for Transit-Oriented Development. In particular, it should be clear if the large Potomac Mills site will have a High-Capacity Transit station at one edge, because portions of that property could end up more than one-half mile from a station.
8) The Quartz development at the intersection of Minnieville Road and Prince William Parkway, and the intersection of Dale Boulevard-Minnieville Road should not be designated as “MultiMobile Hubs” if those sites will not have a High-Capacity Transit station. Bus stops with commuter lots technically might be “multimobile,” but should not be planned for the same level of development as sites with a High-Capacity Transit station.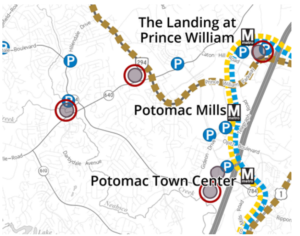
Proposed “Future Transit Alternatives” for Eastern Prince William County
9) Plans for town centers with T-5 and T-6 Transect Zones should be included in the Land Use Map for all sites in eastern Prince William where a High-Capacity Transit station is planned.
10) Action strategies in the Mobility Chapter should identify how to obtain local, state, and Federal funding for extension of Metrorail to Prince William, creation of a Bus Rapid Transit system and shuttle/trolley systems, and development of infrastructure for the proposed commuter ferry.
11) The Land Use Map should identify where affordable housing is planned within walking distance of planned High-Capacity Transit stations, in order to meet the MWCOG targets. Families are cost-burdened if housing costs exceed 30% of Area Median Income, but also cost-burdened if housing and transportation costs combined exceed 42% of Area Median Income.
12) The 2040 Comprehensive Plan should quantify the shortage of affordable housing units for families earning 30%, 50%, and 80% of Area Median Income now, and the projected shortage in 2030 and 2040. The Land Use Map should identify where new affordable housing will be developed by 2030 and 2040 to eliminate the shortage of affordable housing in those three categories, and those locations for new affordable housing should be planned within walking distance of High-Capacity Transit stations.
13) More-detailed shuttle/trolley routes and boundaries of areas where service is planned should be identified on the Future Transit Alternatives Map. The Mobility Chapter should include an action strategy to complete and update regularly origin and destination studies for proposed shuttle/trolley routes, in order to integrate the Mobility Chapter with other 2040 Comprehensive Plan chapters and with the Comprehensive Plans in the Cities of Manassas and Manassas Park. Shuttle/trolley routes should be structured to connect Activity Centers as defined by MWCOG and also nodes of existing/planned dense development as shown on the Land Use Map.
14) An action strategy should be included in the Mobility Chapter to identify the year when shuttle/trolley service will become operational, so rezonings and construction plans can be synchronized.
15) If “[s]pecific objectives include adapting to changing mobility trends, improving multi-modal options, increasing the use of public transit, increasing travel time reliability while concurrently striving to decrease the use of vehicle fuels that contribute to climate change,” then the Mobility Chapter needs to add Local and Express Bus Service maps showing areas to be served by bus service and the stages in which that service will be expanded over the next 20 years. Upgrading local bus service to facilitate access to local jobs, schools, healthcare, retail, and other key destinations for less-advantaged households is at least as essential as extending commuter rail routes that carry white-collar workers out of Prince William. Upgrading low-cost local transit and upgrading bike/pedestrian access offers the greatest opportunity to invest in upgrading equity. Fairfax Connector Transit Strategic Plan Update offers an understandable format that can be used to support comprehensive plan update effort
16) “High-Capacity Transit”, as identified on this map, should be adequately defined in terms of weekday boardings, peak-period headways, and service hours. Bus service that operates for fewer than 16 hours on weekdays, has peak-period headways longer than 15 or 20 minutes, or experiences fewer than 500 daily boardings is merely ordinary transit service.
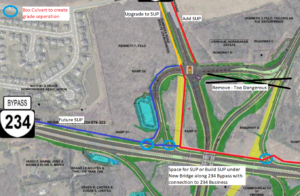
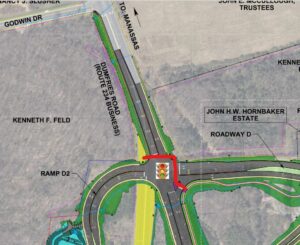
17) The “High-Capacity Transit” lines in the western part of the county, which lack connections to Downtown Manassas, the Manassas Park City Center, the Godwin Drive Technology Corridor, and Sudley Road/Route 234 Business, are missed opportunities. Recommend coordinating with Omniride which represents the entire Greater Manassas area.
###